The Shortcut module provides a toolbar on the top of the page to which you can add links. This is useful for creating links to commonly-used pages within your site. You can organize these links in multiple sets of shortcuts.
Uses
Managing shortcuts
By default, two links are available in your shortcut toolbar: "Add content" and "Find content". To add and edit shortcuts click the "Edit shortcuts" link in the toolbar.
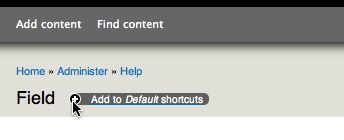
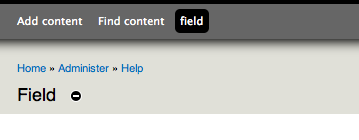
The core Seven administration theme displays a + sign next to administrative page titles that allows you to create a shortcut to that page. (With the overlay module active, the page title appears above the overlay, not under the breadcrumbs as you see here.) If the page is already part of your shortcut set, the link will be a - sign, to remove the shortcut.
Once you've added it, you'll see the new link in your shortcut bar:
To manage shortcuts, you must have the Administer shortcuts permission.
Shortcut set limits
By default, you can only have 7 shortcuts displayed (others can be in the list of shortcuts, but disabled). This is governed by the Drupal variable 'shortcut_max_slots'; like any other Drupal variable, you can update it by using the
drush command-line utility, or in the $conf section of your settings.php file. (Note: you may need to clear the Drupal cache after using either method to update this setting.) See also
this issue on the set size limit.
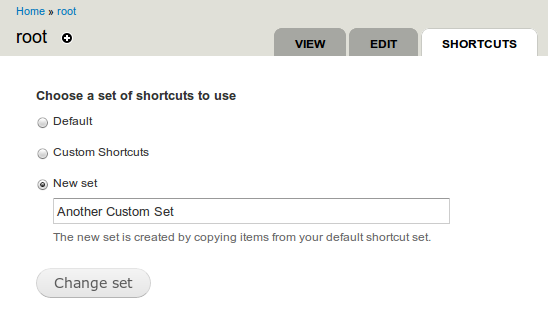
Managing shortcut sets
You can organize shortcuts in sets. To add or edit shortcut sets, navigate to your account page (http://www.example.com/user) and click the "Shortcuts" tab. Only one shortcut set can be displayed at one time.
Displaying and hiding shortcuts
The core
Toolbar module displays the shortcuts near the top of the page, along with an Edit shortcuts link. The shortcuts can be quickly hidden by clicking the arrow sign in the toolbar.
You can display the shortcuts somewhere else in your site by enabling the Shortcuts block on the Blocks administration page (Administer > Structure > Blocks).
Disabling Shortcut module
You can also disable the shortcut feature completely by disabling the module on the modules administration page (Administer > Modules).